What is RAL?
Data has become an important asset of a company. And more and more it distinguishes a company from another, depending on how effective data is managed and analysed. However; data is a common target for unauthorized access. Hackers from the outside or even internal misuse compose a severe threat to data security.
The Read Access Logging (RAL) is a security tool for SAP NetWeaver Application Server ABAP that enables you to monitor and log read access to sensitive or classified data. The purpose is to protect business data and prevent security violations.
In my opinion, RAL is a significant complement functionality for SAP Security framework in order to comply with various standards and regulations.
Business Challenges
To prevent any data security violations, you need to comply with legal and organizational requirements as well as industry standards, for example in banking, insurance and healthcare applications. In addition, data privacy regulations such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) demand a lot from organizations. GDPR is about protecting and restricting access to personal data. If no trace or log is kept on who accesses which data – it is utmost difficult to trace the responsible person for any data leaks or violations.
When a company or public institution want to monitor access to classified or other sensitive data; you need to promptly be able to identify:
- Who had access to the data in a business entity, for example to an insurance account?
- Who accessed personal data, for example a business partner?
- Which personal data was accessed, eg data related to religion, politics etc?
- Who did a data search, for example, if a VIP was admitted to hospital?
- Which accounts, or business partners were accessed by which users?
These questions can be answered by using information about who accessed which data at a specified time. For this purpose: RAL is a tool that can help to determine who accessed which data.
Use Cases
Example 1: Roger is a Data Security Officer in an insurance company. He has been asked to investigate an incident which shows that malicious order payment transaction searches have been made about customers. Before the incident; the insurance company identified all order payment transactions as business critical, they created related RAL-configuration based on logging purpose, that defines the use cases and the reason for the recoding. This enables Roger to find answers in his investigation.
Example 2: Annika is a Compliance Manager in a Pharma company. A customer has complained that her account details has been used to contact her on private issues by an employee of the Pharma company. Annika was asked to identify who had access to the customer’s person related data – and is able to provide her customer with an answer without extensive investigation.
How to set it up?
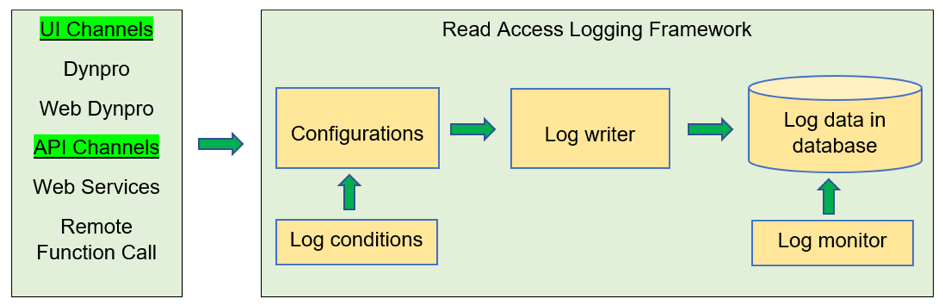 So – how does it work?
So – how does it work?
All remote API and UI infrastructures (that access the data) must be enabled for logging.
The RAL-Manager offers two tabs. First, you need to access Administration tab area: here you can configure which fields and elements that are relevant for logging based on purpose. You need to enable logging. Due to this configuration, the system gathers read access to the specified field elements in a log file. The log is stored in the database. Secondly, you need to allow access to Monitor tab to view the logging results.
Roger and Annika are now able to analyse the log data to determine the source of the information leak!
Sum-up
The purpose of writing this blog post is to create an understanding of how RAL helps a company comply with legal regulations and business standards related to data security. GDPR is the most stringent personal data privacy regulation we are experiencing so far. RAL is an effective tool to comply with who accesses which personal data, when, where and for continuous monitoring. RAL can be used as an important tool to help comply with GDPR.